Current Data on Monoclonal Antibodies and Fc Fusion Proteins
Bill Strohl has an antibody database in which he tracks the current status of clinical stage antibodies, bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, immunocytokines, radioimmunotherapeutics, and chimeric antigen receptor-based cell constructs. He is also in the process of building out a detailed gene therapy database as well. Some the data from Bill’s database were presented in his April 30, 2017 presentation on Target discovery for antibodies.
For example, Bill generated a nice figure on the FDA approved drugs, showing the increase in biologics approved in just the past few years. Small molecule drugs (blue lines), biologics including vaccines (green lines), and monoclonal antibodies/Fc fusion proteins (red lines) approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration from 1997 to May 1, 2017. This information was sourced and extracted from the US FDA website: (https://www.fda.gov/drugs/developmentapprovalprocess/druginnovation/ucm537040.htm).
A nice high-level figure showing different types of antibody-based constructs. A. IgG monoclonal antibody; B. FAb fragment; C. Single chain fragment, variable (scFv); D. Heterodimeric IgG-based bivalent, bispecific antibody; E. scFv-based bispecific antibody such as a BiTE (“bispecific T-cell engager”); F. IgG-scFv-based tetravalent, bispecific antibody; G. Tetravalent scFv-based antibody called TandAb; H. IgG-based Immunocytokine (cytokine is denoted by green oval); I. Tandem scFv-immunocytokine (cytokine is denoted by green oval); J. Fc-peptide fusion (peptides denoted by squiggled lines); K. Fc-protein fusion (protein denoted by gray oval); L. Antibody drug conjugate with three parts (antibody, linker, cytotoxic drug); M. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T based antibody (scFvs on surface of recombinant T cell; examples of intracellular domains noted in box).
Legend:
A. IgG monoclonal antibody; B. FAb fragment; C. Single chain fragment, variable (scFv); D. Heterodimeric IgG-based bivalent, bispecific antibody; E. scFv-based bispecific antibody such as a BiTE (“bispecific T-cell engager”); F. IgG-scFv-based tetravalent, bispecific antibody; G. Tetravalent scFv-based antibody called TandAb; H. IgG-based Immunocytokine (cytokine is denoted by green oval); I. Tandem scFv-immunocytokine (cytokine is denoted by green oval); J. Fc-peptide fusion (peptides denoted by squiggled lines); K. Fc-protein fusion (protein denoted by gray oval); L. Antibody drug conjugate with three parts (antibody, linker, cytotoxic drug); M. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T based antibody (scFvs on surface of recombinant T cell; examples of intracellular domains noted in box)
An updated figure on the market sizes of various categories of biologics, showing the importance of antibodies and Fc fusion proteins in the growth of biologics:
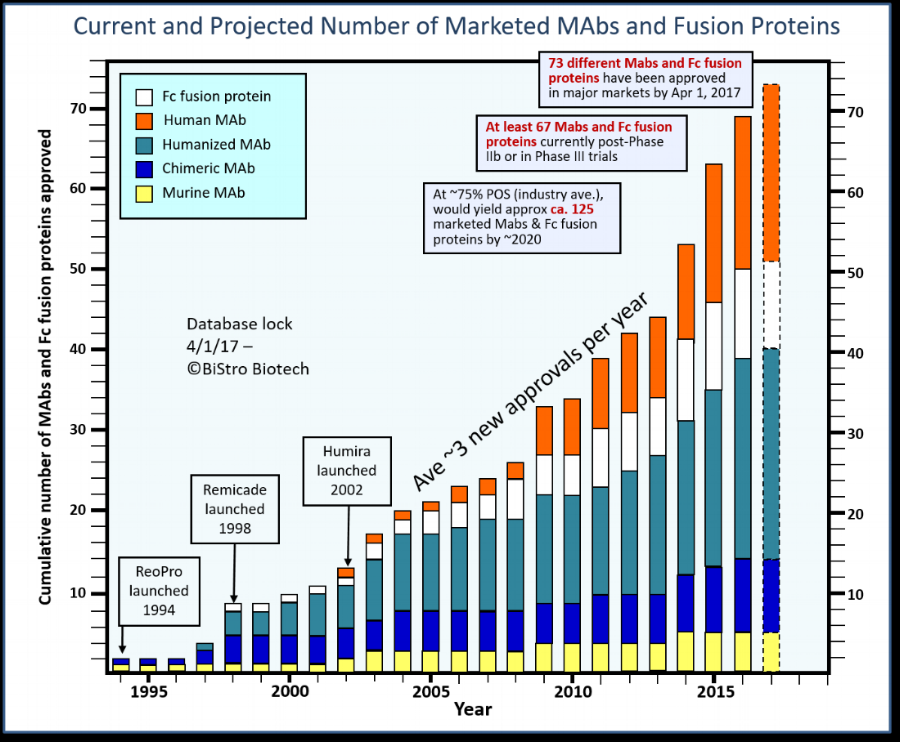
An updated figure on the growth of antibodies and Fc fusion proteins approved by regulatory agencies:
A table showing the numbers and types of antibodies, including bispecifics, ADCs, immunocytokines, Fc fusion proteins, and radioimmunotherapeutics, as well as chimeric antigen receptor recombinant cell constructs in clinical trials.
A table showing the breakdown of the 325 unique target antigens by therapeutic area to which clinical stage antibodies, Fc fusion proteins, and CARs are targeted: